The manufacturing industry is undergoing a seismic shift, and at the heart of this transformation is robotics. Once confined to repetitive tasks in automotive assembly lines, robots are now smarter, more adaptable, and increasingly collaborative. As we look to the future, robotics is poised to redefine how factories operate, how products are manufactured, and how humans and machines collaborate.
In this new era of automation and robotics, manufacturers are turning to intelligent robotic systems to improve product quality, reduce downtime, and meet growing demands for efficiency. Whether it’s industrial robots enabling high precision in assembly or collaborative robots enhancing safety on the production line, the benefits of robots in manufacturing are clear. These innovations not only boost performance at a high level, but also contribute to reducing the risk of injury, optimizing workflows, and supporting long-term transformation across the manufacturing industry.
From automation to intelligent robotic systems: the path to autonomy
Traditional industrial robots were designed for speed and high precision, but they lacked flexibility. Today’s robots are evolving into autonomous systems capable of learning, adapting, and making decisions in real-time. Powered by AI and machine learning, these robotic applications can now:
- Detect and respond to changes in their environment
- Optimize their own performance
- Collaborate safely with human workers (cobots)
This shift from automation to autonomy enables mass customization, faster production cycles, and reduced downtime.
Collaborative robots: safer, smarter manufacturing
One of the most exciting developments is the rise of collaborative robots, also known as cobots. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which operate in isolation, cobots are designed to work side by side with humans. They are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features that allow them to:
- Assist with complex assembly tasks
- Reduce physical strain on workers
- Learn from human input and improve over time
This human-robot collaboration is not about replacing jobs; it’s about enhancing human capabilities, reducing the risk of injury, and creating safer, more efficient workplaces where robots work in harmony with people.
How IoT and robotics are shaping the smart factory
The integration of robotics with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is unlocking new levels of connectivity and intelligence. As automation and robotics evolve, robots can now communicate with other machines, systems, and even supply chains. This connectivity enables:
- Real-time monitoring and diagnostics
- Predictive maintenance
- Seamless inventory and logistics management
In essence, robots are becoming an integral part of the smart factory ecosystem – transforming the manufacturing industry and driving greater efficiency across every production line.
Robotics and automation gain momentum in 2025 tech investment trends
In Alithya’s recent survey of more than 135 manufacturing professionals across various sectors, participants were asked which area of technology investment will be the highest priority for their company in 2025. Approximately 24% ranked robotics and automation as their top priority behind AI and machine learning, cybersecurity, data protection, and supply chain optimization tools.
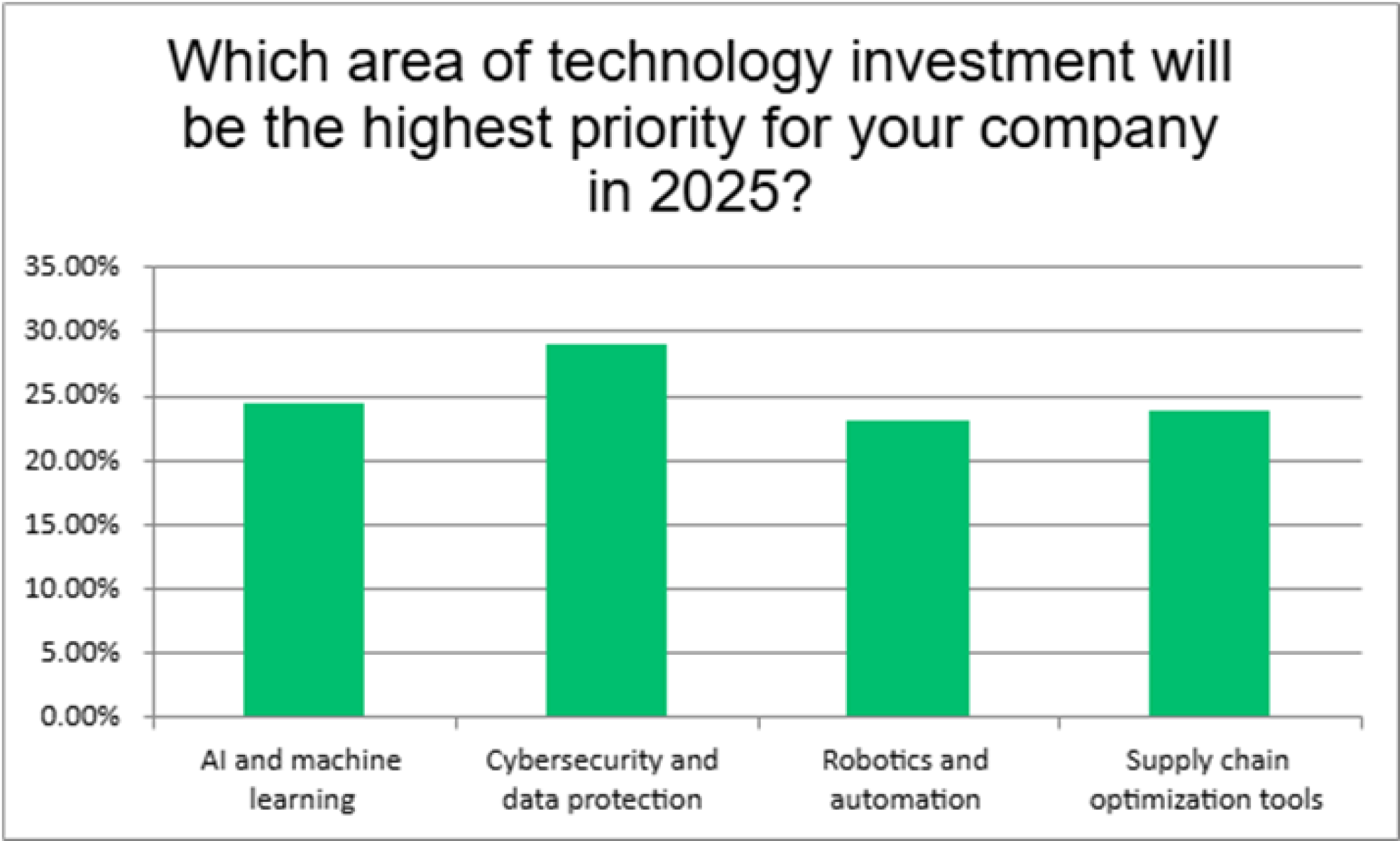
That percentage is expected to increase rapidly, based on the speed and precision that robotics can bring to the manufacturing process while also helping to address labor shortages, enhance job satisfaction, increase productivity, and drastically reduce production errors. View more findings from the survey here – Alithya’s 2025 Manufacturing Survey Report and Analysis.
How Microsoft and Oracle power intelligent robotics in manufacturing
Microsoft technologies
Microsoft is playing a pivotal role in enabling intelligent robotics through its Cloud for Manufacturing, Azure AI, and Microsoft Fabric platforms.
- Azure AI + Copilot for Factory Operations: Manufacturers can build custom copilots that help frontline workers interact with robotics systems using natural language—for tasks like asset maintenance, issue resolution, and training.
- Microsoft Fabric: This end-to-end analytics platform helps unify operational and IT data, enabling real-time insights and AI-driven decision-making across robotic systems.
- Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management: Enhance traceability and integrate seamlessly with robotic systems to optimize production and logistics with D365 SCM.
Oracle technologies
Oracle supports robotics and automation through its Oracle Cloud SCM and IoT-enabled applications:
- Oracle IoT Production Monitoring Cloud: Provides real-time visibility into robotic equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Oracle Autonomous Database: Powers data-driven robotics by managing and analyzing massive volumes of sensor and machine data with minimal human intervention.
- Oracle Digital Twin and AI Apps: Simulate robotic workflows and optimize factory layouts to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Together, these platforms enable a new era of connected, intelligent, and autonomous manufacturing.
Emerging robotics trends shaping the future of manufacturing
Several global trends are accelerating the adoption of robotics in manufacturing:
- Labor shortages: As skilled labor becomes harder to find, robots are filling critical gaps. As AI and robotics take over repetitive and hazardous tasks, workers can focus on higher-value activities, such as system oversight and optimization.
- Reshoring: Companies are bringing production closer to home, and robotics makes local manufacturing more cost-effective.
- Sustainability: Robots can optimize energy use and reduce waste, supporting greener manufacturing practices.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see:
AI-powered robotic swarms for flexible, decentralized manufacturing
Imagine a factory floor where dozens—or even hundreds—of small, intelligent robots work together like a colony of ants. This concept is the basis for robotic swarms. Inspired by nature, these robots offer the following benefits in manufacturing:
- Flexibility: Robotic swarms can adapt to different tasks and environments, making them suitable for custom or small-batch production.
- Scalability: Adding more robots to the swarm can increase production capacity without significant changes to the infrastructure.
- Resilience: The decentralized nature of swarms enables the system to continue functioning even if individual robots fail.
- Efficiency: Parallel task execution by multiple robots can reduce production time and increase throughput.
The swarm robotics market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in AI and the increasing demand for intelligent manufacturing solutions. Projections indicate the market could reach $3.0 billion by 2028.
Self-repairing robots that minimize downtime
Downtime is one of the costliest issues in manufacturing. Self-repairing robots aim to solve this by:
- diagnosing their own faults using embedded sensors and AI,
- performing basic repairs autonomously, such as recalibrating joints or replacing modular components, and
- alerting human technicians only when intervention is absolutely necessary.
Some advanced systems even use 3D printing to regenerate worn-out parts on the spot. This innovation reduces the need for constant human oversight and extends the lifespan of robotic systems, leading to lower maintenance costs and higher uptime.
Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) models that lower the barrier to entry
Traditionally, implementing robotics systems has required a significant upfront investment— encompassing hardware, software, integration, and training. RaaS changes that by offering:
- subscription-based access to robotic systems,
- cloud-based control and analytics, often managed by the RaaS provider, and
- scalability to add or remove robots as needed.
This model is especially beneficial for small and mid-sized manufacturers who want to stay competitive but lack the capital for full-scale automation. RaaS providers often include maintenance, updates, and support, making it easier for businesses to adopt robotics without deep technical expertise.
Why robotics in manufacturing is your next strategic advantage
Robotics is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a present-day reality reshaping the manufacturing landscape. The future of robotics in manufacturing is not just about machines; it's about creating a more resilient, agile, and human-centric industry.
Companies that embrace this technology will not only boost productivity but also gain a competitive edge in an increasingly dynamic market. Are you ready to welcome the robots?
Alithya’s team of manufacturing technology experts is ready to develop a digital strategy that streamlines processes and operations while optimizing user adoption and customer experiences. We meet you where you are, focusing on helping you achieve your goals and desired business outcomes on the technology platform that best suits you. We invite you to collaborate with our consultants and re-imagine what’s possible.
Key sources and references
Universal Robots - Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Microsoft.com - Microsoft Cloud for Manufacturing
Microsoft Tech Community - Azure AI and Copilot for Manufacturing
Learn.microsoft.com - Microsoft Fabric for Unified Analytics
Oracle.com - Oracle Autonomous Database
Oracle.com - Oracle Digital Twin and AI Applications
Robotics Tomorrow - Robotic Swarms in Manufacturing
Science Robotics - Self-Healing Robots
ABI Research - Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS)
